Network analysis
Bolzano
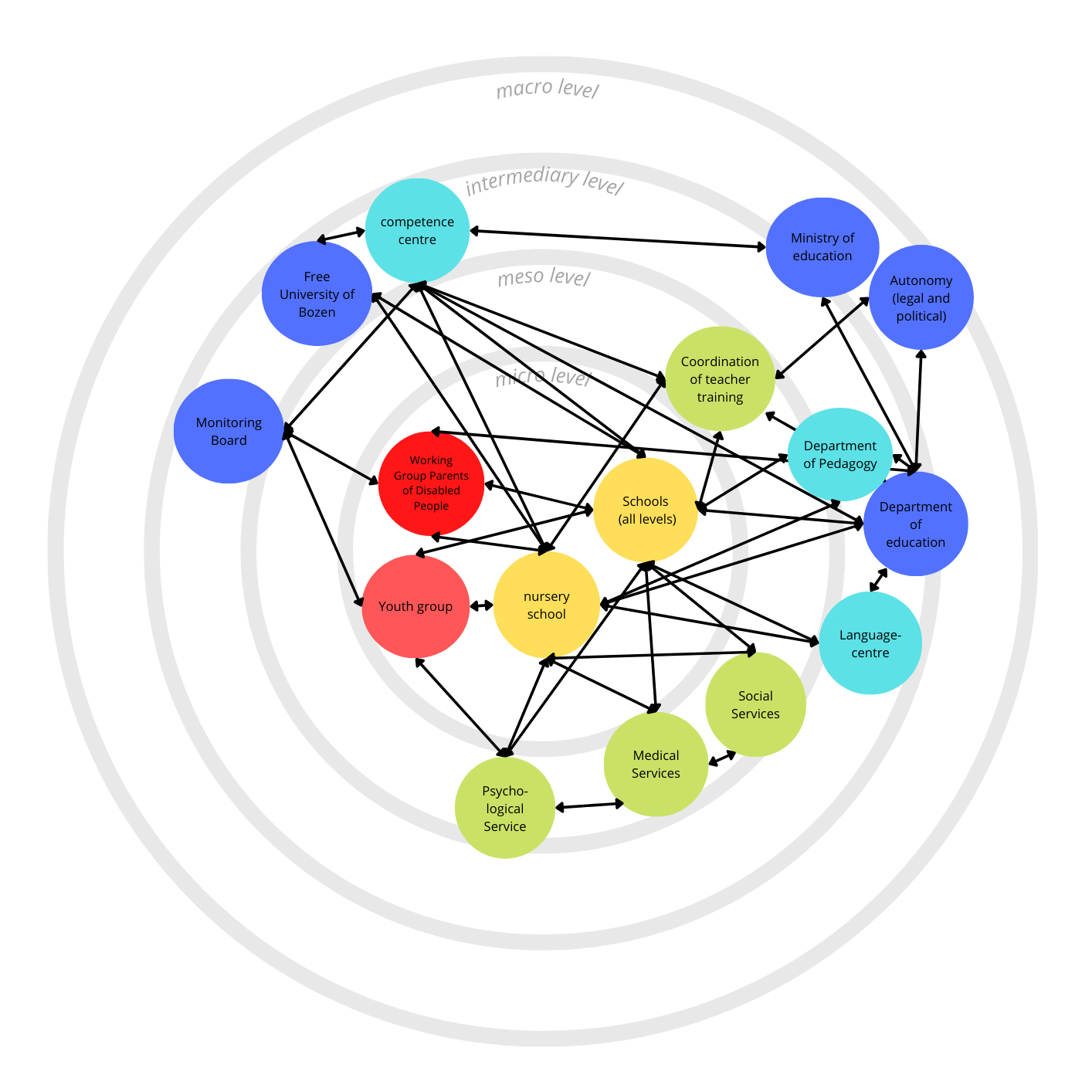


























Representation of the actors and agents involved in the Governance of Inclusive Education in the school system and participating in the Round-Table-Meetings in the school administration region South Tyrol within the international project.
Text description of the network analysis
The image is a complex diagram showing the relationships and interactions between various educational entities across different levels, from micro to macro.
At the micro level, the diagram features “Primary schools” and “Secondary schools” as central nodes, with “Primary schools” connected to “School district primary school,” “Medical Services,” and “Social Services.” The “Secondary schools” are linked to “Coordination of teacher training.” Both school types are also connected to a node labeled “Psychological Service.”
The meso level includes “Working Group Parents of Disabled People” and “Youth group,” which are highlighted in red, indicating their importance or focus in this context. These groups are interconnected with the micro-level schools and the “Psychological Service.”
At the intermediary level, there are entities such as “Universities with competence centers,” “Ministry of education,” “Federal States,” “Department of education,” and “Regional Language Centre.” These are depicted as nodes connected to each other and to the meso and micro levels, suggesting a system of governance and specialized support services.
The macro level features a single entity: the “Monitoring Board,” which is connected to the “Universities with competence centers” and the “Ministry of education.”
Black lines connect the various nodes, illustrating the network of communication or operational pathways among these entities. The concentric circles categorize the entities by their operational scope within the educational system, with individual groups and schools at the micro-level and overarching organizations like the “Monitoring Board” at the macro level.
Entity descriptions
Monitoring Board
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international treaty in which the signatory States undertake to promote, protect, and guarantee the human rights of persons with disabilities. Italy signed the treaty in 2007. In South Tyrol, it was adopted by provincial law no. 7 of 14th July 2015. This provincial law established the South Tyrolean Monitoring Committee for the Rights of Persons with Disabilities. Since 2020, the South Tyrolean Monitoring Committee is regulated by Article 32 of Provincial Law No. 11 of 9th October 2020. The main task of the Monitoring Committee is to promote and monitor the implementation of the UN Convention in South Tyrol.
Universities with competence centres
The Competence Centre for Inclusion in Education is dedicated to research, networking, and scientific exchange on inclusive education. Inclusion research aims to provide analyses of and conceptual answers to the differences and diversity of all children and pupils. The aim is to guarantee the full participation and learning of each and everyone, with a particular focus on identifying and removing possible cultural, structural, or practice-related barriers in educational institutions.
The main objective of the centre is to conduct research in the field of inclusion in education at regional, national, and international level. The exceptional geographical and cultural location of the Free University of Bozen offers particularly interesting perspectives for research, networking, and scientific exchange on inclusive education.
The competence centre aims to contribute to this through various research activities:
- bringing knowledge and findings on the Italian and South Tyrolean inclusive education sector to the international scientific debate
- strengthening the development of inclusion in kindergartens and schools in South Tyrol through practice-relevant research.
Ministry of education
The MIUR is the Italian Ministry of Education, literally translated “Ministry of Education and Merit”. It is responsible for the functions and tasks assigned to the State in the areas of school and university education and higher artistic, musical and dance education as well as scientific and technological research.
Federal States
The schools were given autonomy in the areas of didactics, organisation, research, school development, administration, and finance. With effect from September 1st, 2000, all public schools in the region were granted legal personality. They thus became legal entities under public law.
Working Group Parents of Disabled People
Active Parents of People with Disabilities is an association of affected parents of people with disabilities for self-help. Its main aim is to represent the interests of people with disabilities, carry out political work and provide advice and support.
Secondary schools
In South Tyrol and Italy, schooling is compulsory for all children for 8 school years from the age of 6: from 6 to 10, children attend elementary school (grades 1 to 5), and then secondary school (grades 6 to 8, lower secondary school level) until the age of 13. Years 9 to 13 comprise upper secondary schools and vocational schools (upper secondary school level). Education is compulsory until the age of 18.
Department of education
The German-speaking Directorate of Education is an institution of the Autonomous Province of Bozen – South Tyrol. It is specifically responsible for the organisation and administration of the German-language education system in South Tyrol. In addition to the German-speaking directorate of education, there are also an Italian-speaking and a Ladin-speaking Directorate of Education. The Directorate of Education is responsible for various aspects of education, including school planning, school development, curricula, teaching materials, teacher remuneration and monitoring school quality. It ensures that schools teaching in German receive the appropriate resources and support to meet the educational needs of the German-speaking population. It is important to note that South Tyrol is featured by a complex ethnic and linguistic diversity, which is also reflected in the education system.
Youth group
The youth group of the Association of Parents of Hearing-Impaired Children is led by two educational staff members. They support the young people from the Association of Parents of Hearing-Impaired Children in a wide variety of areas, e.g., on their way into the job market, with various everyday matters, with leisure and further education offers, through consultancy on better communication support and on the use of technological aids, through the exchange among affected people to strengthen their personality.
Primary schools
In South Tyrol and Italy, schooling is compulsory for all children for 8 school years from the age of 6: from 6 to 10, children attend elementary school (grades 1 to 5), and then secondary school (grades 6 to 8) until the age of 13. Education is compulsory until the age of 18.
Regional Language Centre
The languages centres inform families with migration background and their children about the organisation of the education system and the various educational opportunities in South Tyrol. They support kindergartens and schools of the region South Tyrol in promoting language learning and inclusion. They make a concrete contribution to ensuring that all children and young people have the same educational opportunities. The implementation concept for the new resolution, which was drawn up by the provincial government in 2020, sets out the areas of activity, objectives and focus of the languages centres. The languages centres are coordinated by a steering group made up of employees from the German and Italian Directorate of Education and from the Ladin Culture and Education Directorate.
Psychological Service
The Psychological Service and the psychological staff of the service are available to actors responsible for education about specific questions about child development or in problematic situations. Parents receive counselling and support, for instance, in the event of behavioural problems and of problems with learning and performance. Upon request of kindergartens and schools, the Psychological Service makes diagnoses in consultation with those responsible for education.
Social Services
In South Tyrol and in all Italy, Sozialsprengel (social services districts) are local organisations that provide health and social services at municipal level. These institutions were created to organise healthcare and social services efficiently and in line with the local needs. The tasks of the Sozialsprengel include the following areas:
- Healthcare services: Sozialsprengel are responsible for providing basic medical and healthcare services in their respective municipalities. This can include the provision of outpatient medical services, the organisation of vaccination programmes, health promotion and prevention as well as support in caring for elderly or sick people.
- Social services: Sozialsprengel offer support and services in the social field. This can include looking after children and teenagers, supporting families in crisis situations, accompanying elderly people, promoting the integration and inclusion of people with disabilities or migrants and organising educational and leisure activities.
- Care services: Sozialsprengel are often also active in organising care services to help older people and people with special needs. This includes home care, day care, short-term care and support in organising long-term care.
- Counselling and support: The Sozialsprengel provide counselling and support for individuals and families in social and health matters. This can include help with applying for social benefits, legal support, or psychological counselling.
Medical Services
Italy has a regional healthcare system in which the various regions are largely autonomous in their responsibility for the organisation and provision of healthcare services. The South Tyrolean Healthcare Service is the healthcare organisation responsible for the provision of healthcare services in South Tyrol. It operates hospitals, clinics, medical practices, and other healthcare facilities and provides medical care for citizens.
This work is licensed under Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International