Network analysis
Steiermark
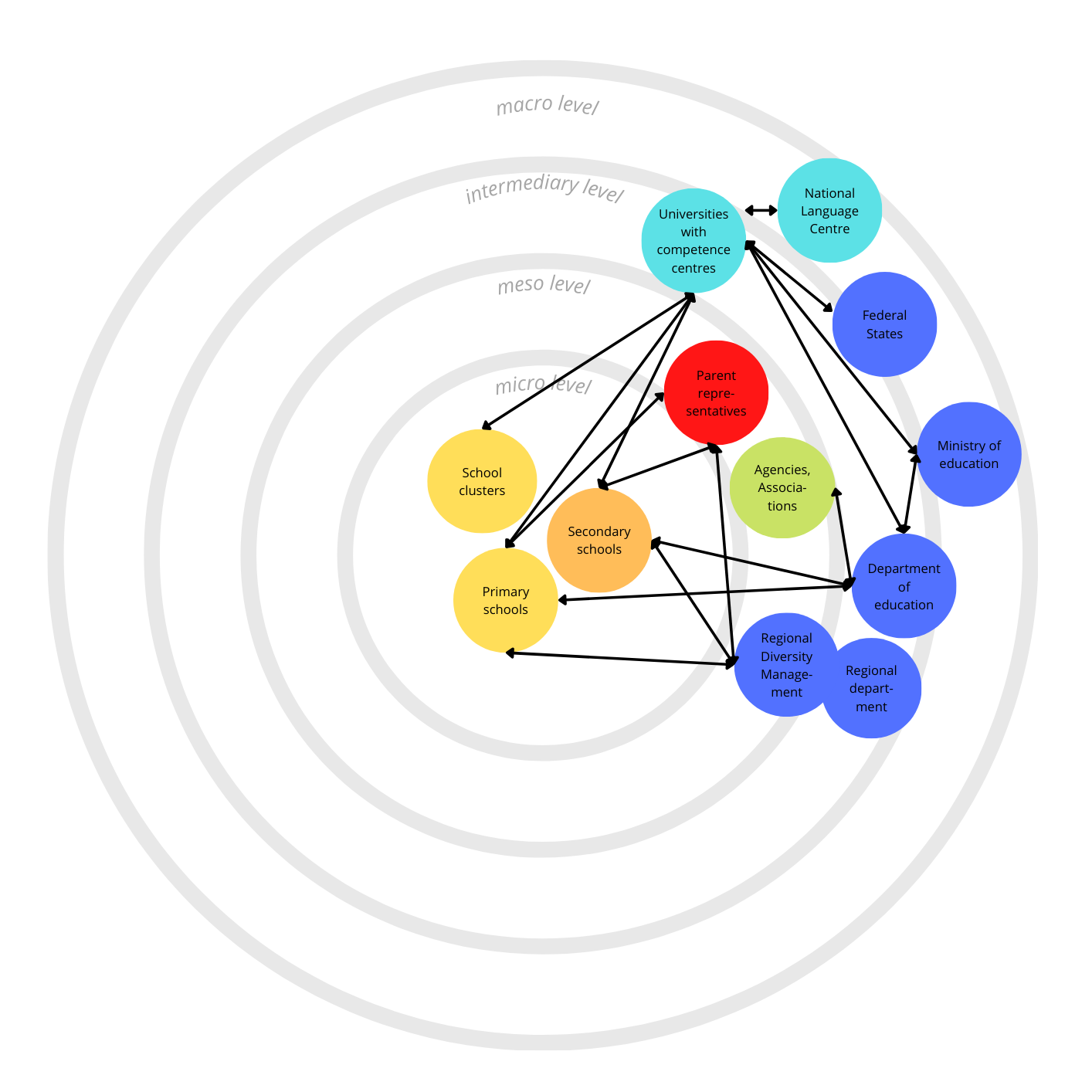
























Representation of the actors and agents involved in the Governance of Inclusive Education in the school system and participating in the Round-Table-Meetings in the school administration region Styria within the international project.
Text description of the network analysis
The image presents a diagram mapping the hierarchical relationships in an education system, organized across four levels: micro, meso, intermediary, and macro.
At the micro level, there are three primary nodes: “School clusters,” “Primary schools,” and “Secondary schools.” These are depicted in yellow, except for “Secondary schools,” which is linked to “Parent representatives,” highlighted in red, indicating a special focus or importance.
The meso level consists of a single entity, “Agencies, Associations,” which is connected to “Secondary schools” and another node at the intermediary level.
At the intermediary level, we see several nodes: “Universities with competence centres,” “National Language Centre,” “Federal States,” “Ministry of education,” “Department of education,” “Regional department,” and “Regional Diversity Management.” These are in blue and are interconnected among themselves and also with “Parent representatives” and “Agencies, Associations.”
Finally, the macro level does not contain any specific entities but encircles all levels, suggesting an overarching scope.
Lines interconnect the various nodes, signifying the network of influence or communication pathways among the entities. The arrangement of nodes within the concentric circles indicates their role and operational scope within the educational system, from the direct educational environment at the micro level to the broader organizational and governance structures at the intermediary level.
Entity descriptions
Universities with competence centres
A competence centre is a research platform in which companies and scientific partners (universities, universities of applied sciences, research institutions) bundle and build up research capacities. The content is aligned with a jointly defined research programme and is based on the standards of top international research.
National Language Centre
The Austrian Language Competence Centre is a specialised institute for language learning and teaching commissioned by the Ministry of Education. It supports school teams and educational authorities in the organisation and further development of equal language education chances in step with the times through high-quality products and flexible services. It promotes language education from kindergarten to school-leaving examination and beyond with a wide range of measures:
- Creating practical materials that are based on current research developments in language teaching/learning and can be used directly in the classroom.
- Networking stakeholders within the education system and promoting co-operation at events.
- Providing knowledge in further education and training initiatives and programmes.
- Campaigns and competitions provide a stage for innovative language initiatives and projects and promote multilingualism.
Parent representatives
Parents have the right to elect representatives who act as an interface with teachers, school management, and school authorities. Parent representatives have co-determination and participation rights. They must be informed about laws, regulations, and decrees by the school management.
Federal States
The federal or federally organised State of Austria is made up of nine federal provinces (Vienna, Lower Austria, Upper Austria, Burgenland, Styria, Carinthia, Salzburg, Tyrol, and Vorarlberg). In contrast to a centrally organised State, in a federal State legislation and low enforcement are divided between the federal State and federal provinces. The governments of federal provinces are responsible for the provincial administration as well as for the implementation of many federal laws in the federal province.
School clusters
A school cluster is the organisational and educational merger of two to a maximum of eight schools in geographically neighbouring locations under a common leadership and management. Each school remains as such and is strengthened by the co-operation within the cluster. The school cluster management takes over the tasks of the previous school management. Each school continues to have a contact person (area leader), who supports the cluster management at the specific location.
Ministry of education
The Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Research is responsible for the education system from kindergarten to adult education. This ministry is also responsible for research, school quality and school law. It represents the interests of Austria as a centre of science, research, and education at an international level.
Primary schools
Common school which lasts 4 years for all children from the age of 6 (compulsory schooling). Primary school has the task of providing a common primary education for all pupils, taking into account the social integration of children with disabilities. The aim is to enable children’s access to a basic and balanced education in the social, emotional, intellectual, and physical areas of personality. Children who have reached compulsory school age in the calendar year in question but are not yet deemed ready for school are to be taught in the pre-school grade. The same applies to children whose early admission to the first year has been revoked. The social integration of children with disabilities must be considered. The pre-school grade can be run as a separate programme or together with other school levels.
Secondary schools
Lower secondary level, ISCED 2: In Austria, this ranges from the fifth to the eighth grade and can be completed in special schools, lower grades of general secondary schools, co-operative middle schools, and new middle schools.
Upper secondary level, ISCED 3 and 4: After the lower secondary level, in Austria, there is usually one more year of compulsory schooling, then further schooling is voluntary. The upper secondary level begins with the ninth grade and there are many options for further education. In Austria, this level includes polytechnic schools, vocational schools and apprenticeships – as a dual education system, intermediate vocational schools, higher vocational schools, technical schools and upper levels of general secondary schools.
Department of education
The Department of Education is an administrative authority for all schools, except for agricultural and forestry schools. They are responsible for the implementation of school law, service law and staff representation law. The Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Research is the supreme authority at federal level.
Agencies, Associations
Organisations and groups dedicated to promoting and advancing inclusive practices and policies in the federal province of Styria. These entities collaborate, advocate, and implement initiatives aimed at fostering equal opportunities, diversity, and social integration for individuals with diverse backgrounds and abilities. They work towards creating a more inclusive society by offering support, resources, and programs that address barriers and promote participation.
Regional department
The Styrian Directorate of Education was established on 1st January 2019 as the successor of the Provincial School Board. It is the central education authority responsible for the entire school system in Styria (school law, quality assurance, service law, staff representation law). Moreover, the presidium area of the Styrian Directorate of Education has a school pedagogical service for the purpose of pedagogical-psychological counselling and of coordination of psychosocial support in schools.
Regional Diversity Management
The Diversity Management is the point of contact for inclusion, diversity and special needs education in schools. It understands inclusion as a social and human rights mandate and in this sense contributes to the quality development of a school of diversity. It accompanies processes and transitions (e.g. in challenging situations, when implementing support measures and designing inclusive learning environments), involves pupils, parents, teachers, and extracurricular organisations and offers coordination, moderation, advice, and support. It prepares expert reports and supports the establishment and evaluation of individual support measures and inclusive learning environments.
This work is licensed under Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International