Network analysis
Tübingen
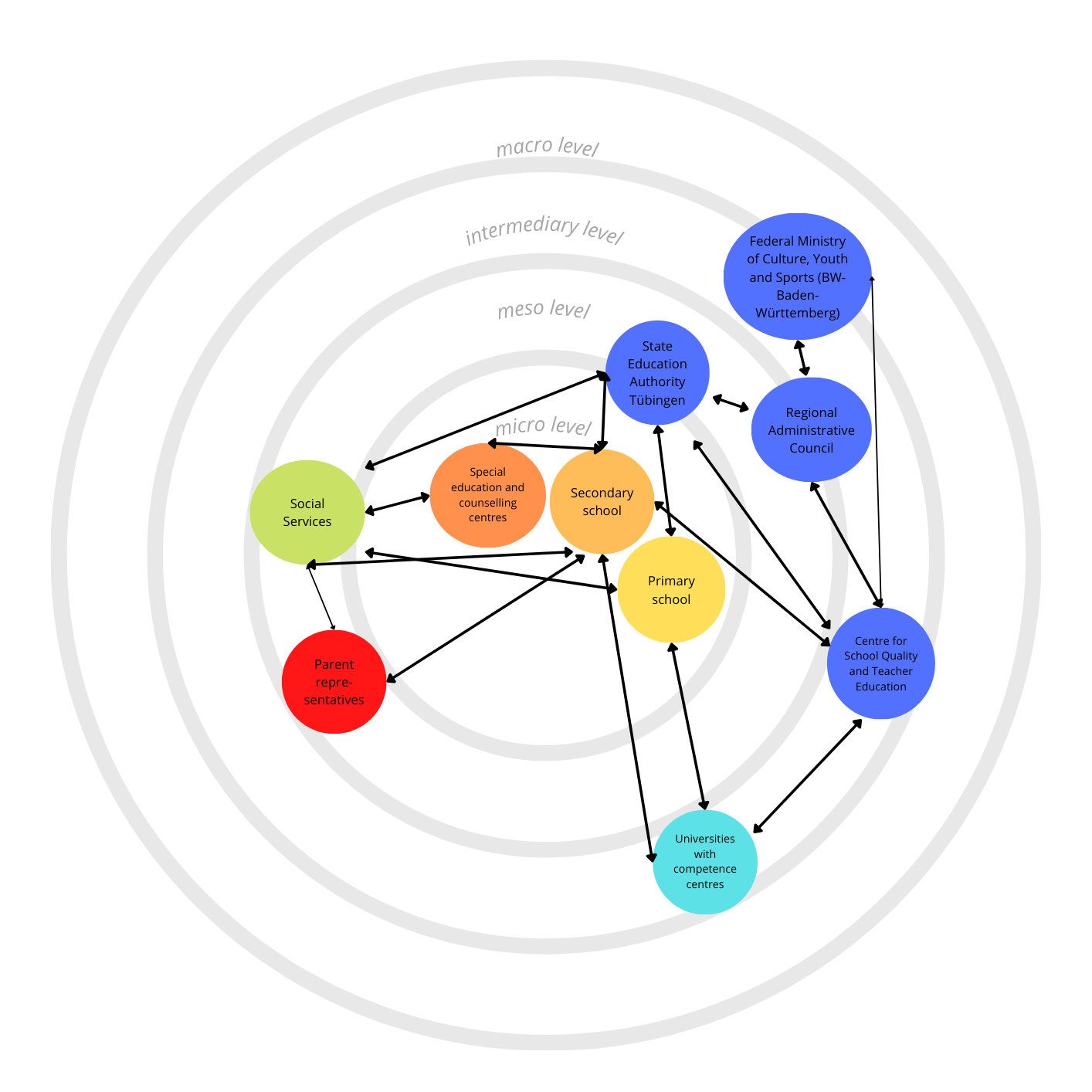




















Representation of the actors and agents involved in the Governance of Inclusive Education in the school system and participating in the Round-Table-Meetings in the school administration region Baden-Württemberg within the international project.
Text description of the network analysis
The layered diagram illustrates the relationships between various stakeholders in an educational system, organized into four concentric levels: micro, meso, intermediary, and macro levels. These levels represent different scales of interaction and influence, from direct local engagement to overarching governance.
At the micro level, the diagram highlights key players directly involved in education and its immediate ecosystem. This includes primary schools, secondary schools, and special education and counselling centres, which are central to the education process. They interact closely with social services, providing additional support, and with parent representatives, who act as a voice for families within the system.
Moving outward to the meso level, the focus shifts to broader institutional support, such as universities with competence centres, which contribute expertise and research to enhance educational practices and teacher training.
At the intermediary level, entities like the State Education Authority Tübingen play a critical role in coordinating and mediating between the local schools and the higher-level administrative bodies.
Finally, the macro level encompasses overarching institutions like the Federal Ministry of Culture, Youth and Sports (Baden-Württemberg), the Regional Administrative Council, and the Centre for School Quality and Teacher Education. These bodies set policies, provide resources, and ensure quality standards across the education system.
The diagram uses arrows to depict the flow of communication, collaboration, and influence between these stakeholders. For example, schools interact with social services and parents at the micro level, while also connecting to higher-level institutions through intermediary structures. The overall image reflects the interconnectedness and complexity of the education system, where each level supports and informs the others to achieve common goals.
Entity descriptions
Federal Ministry of Culture, Youth and Sports (Baden-Württemberg)
The Federal Ministry of Culture, Youth and Sports in Baden-Württemberg is a federal authority responsible for the education, from nursery school to qualification for university entrance. Its remit includes public and private schools, early childhood education, further education and sports. It is responsible for the allocation of teacher resources in inclusive education, for school legislation and other regulations.
State Education Authority Tübingen
The State Education Authority Tübingen is, as the lower school supervisory authority, responsible for primary, technical secondary, real secondary, and community schools as well as for special education and counselling centres in an assigned region. It is responsible for the support of inclusive educational settings in individual schools and for the monitoring. Every education authority has a pool of additional teaching load for inclusive education.
Regional Administrative Council
The regional council is the authority responsible for a specific administrative district and acts as an interface between the government and the local authorities (district administrations, cities and municipalities). A regional council is divided into different departments. The department “School and Education” deals with school and personnel law issues, advises and supports schools in all matters, provides impetus for school development and acts as a school supervisory authority. It is also responsible for planning teacher requirements and managing the state education authorities.
District Office (with two different organisations: ‚Social Security Office‘ and ‘Youth Health Office‘)
District Office (with two different organizations: ‚Social Security Office‘ and ‘Youth Health Office‘): The institutions under the District Office are responsible for the organization of the so called ‚integration assistance‘. They can provide school support for individual children for the participation in education. According to the German Social Code for every person in education with a mental or physical disability.
Special education and counselling centres
The school legislation regulates: Pupils with disabilities and with an ascertained entitlement to special educational offers, if their right to education can’t be fulfilled at mainstreaming schools, they attend a special education and counselling centre. Special education and counselling centres are differentiated according to focal points of support into 9 different categories. They provide their own educational programmes and support regular schools with special educational counselling, support, and education according to the needs. They teach according to different curricula from the mainstreaming curricula.
Secondary school
The secondary school is divided into lower secondary level (grades 5-10) and upper secondary level (grades 11-13). There are at least five different kinds of lower secondary schools (ISCED 2): Hauptschule, Werkrealschule, Realschule, Gymnasium and Gemeinschaftsschule (and the Special Education and Counselling Centres). The school types offer different graded school leaving certificates. In principle, inclusive education (for pupils with disabilities) is possible in all these types of schools. In the upper secondary schools (ISCED 3) differentiated teaching is not planned
Parents
Parents of children with and without Special Needs are important cooperation partners in the planning and implementation of inclusive education and corresponding interventions.
Primary school
The primary school is the common foundational level of the school system. It conveys basic knowledge and skills. Its specific mission is to gradually introduce pupils from playful to school-related forms of learning and work. This includes developing the various talents of the pupils in a common educational programme, practicing the behaviors for living together and promoting the power to construct and express oneself creatively. The primary school comprises four school years. These schools can also offer inclusive education (for pupils with disabilities).
Centre for School Quality and Teacher Education
The core tasks of the Centre for School Quality and Teacher Education are: professional development; executive qualifications; developing concepts and managing the implementation; quality assurance for cross-cutting pedagogical topics, subject- and school-specific topics; conception of teaching support programmes; development of educational plans; approval of textbooks; international cooperation projects in teacher education; development, decentralized provision and quality assurance of advisory services, for example regarding school careers, job orientation, need of additional support and special talents; school psychological services; prevention and quality development of general education and vocational schools. At the Centre for School Quality and Teacher Education so called “Practical Inclusion Facilitators“ (Praxisbegleiter*innen Inklusion PBI) are employed with the responsibility for supporting multi-professional teams in inclusive education settings.
Universities with competence centres
Universities of Education educate prospective teachers in the first stage of their training, except for the Gymnasium and vocational schools. Full Universities are responsible for the education in the first phase of these school types. The teacher education curriculum includes one module on inclusive education, that is not obligatory. At least 6 Credit Points are dedicated to inclusive education (in Educational Science). Special Education Teachers have a load of more credits related to inclusive education. The Universities have so called “Professional Schools of Education” with a focus on teacher education.
This work is licensed under Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International